VLAN Questions
Question 1
Explanation
The Port Fast feature is automatically enabled when voice VLAN is configured. When you disable voice VLAN, the Port Fast feature is not automatically disabled.
Question 2
Explanation
802.1Q VLAN frames are distinguished from ordinary Ethernet frames by the insertion of a 4-byte VLAN tag into the Ethernet header.
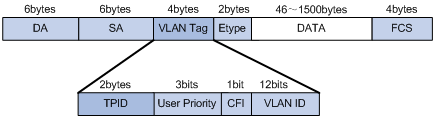
Question 3
Explanation
Because the 802.1Q tunneling feature increases the frame size by 4 bytes when the metro tag is added, you must configure all switches in the service-provider network to be able to process maximum frames by increasing the switch system MTU size to at least 1504 bytes.
Question 4
Explanation
The VLAN ID field inside an 802.1q frame consists of 12 bits. Therefore we have 212 = 4096 VLAN IDs, theoretically.

Question 5
Explanation
Each access port can be only assigned to one VLAN via the “switchport access vlan ” command.
Question 6
Explanation
This command is used to enable tagging of native VLAN frames on all 802.1Q trunk ports.
Answer A is not correct because even when the native VLAN is set to 1, all of the frames of the native VLAN are tagged.
Answer B is not correct because the control traffic still passes via the default VLAN (VLAN 1).
Answer C is not correct because all the frames are tagged with 4-byte dot1Q tag.
Answer D is not correct as “Control traffic continues to be accepted as untagged on the native VLAN on a trunked port, even when the vlan dot1q tag native command is enabled” according to this link: https://www.cisco.com/c/m/en_us/techdoc/dc/reference/cli/nxos/commands/l2/vlan-dot1q-tag-native.html
Question 7
Explanation
When you delete a VLAN, any LAN ports configured as access ports assigned to that VLAN become inactive. The ports remain associated with the VLAN (and inactive) until you assign them to a new VLAN.
Question 8
Explanation
The PortFast feature is automatically enabled when voice VLAN is configured. When you disable voice VLAN, the PortFast feature is not automatically disabled.
Question 9
Question 10


