Question
You work for SWITCH.com. They have just added a new switch (SwitchB) to the existing network as shown in the topology diagram.
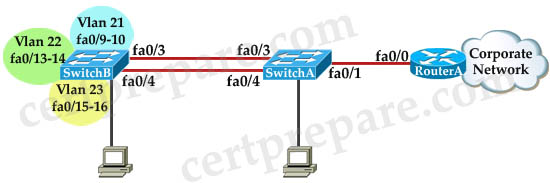
RouterA is currently configured correctly and is providing the routing function for devices on SwitchA and SwitchB. SwitchA is currently configured correctly, but will need to be modified to support the addition of SwitchB. SwitchB has a minimal configuration. You have been tasked with competing the needed configuring of SwitchA and SwitchB. SwitchA and SwitchB use Cisco as the enable password.
Configuration Requirements for SwitchA
– The VTP and STP configuration modes on SwitchA should not be modified.
– SwitchA needs to be the root switch for vlans 11, 12, 13, 21, 22 and 23. All other vlans should be left are their default values.
Configuration Requirements for SwitchB
– Vlan 21, Name: Marketing, will support two servers attached to fa0/9 and fa0/10
– Vlan 22, Name: Sales, will support two servers attached to fa0/13 and fa0/14
– Vlan 23, Name: Engineering, will support two servers attached to fa0/15 and fa0/16
– Access ports that connect to server should transition immediately to forwarding state upon detecting the connection of a device.
– SwitchB VTP mode needs to be the same as SwitchA.
– SwitchB must operate in the same spanning tree mode as SwitchA.
– No routing is to be configured on SwitchB.
– Only the SVI vlan 1 is to be configured and it is to use address 192.168.1.11/24.
Inter-switch Connectivity Configuration Requirements:
– For operational and security reasons trunking should be unconditional and Vlans 1, 21, 22 and 23 should tagged when traversing the trunk link.
– The two trunks between SwitchA and SwitchB need to be configured in a mode that allows for the maximum use of their bandwidth for all vlans. This mode should be done with a non-proprietary protocol, with SwitchA controlling activation.
– Propagation of unnecessary broadcasts should be limited using manual pruning on this trunk link.
Note: There is a requirement that the trunk between SwitchA and SwitchB must be configured under physical interfaces, not logical port-channel interface
Answer and Explanation:
Read more…
You have been asked to install and configure a new switch in a customer network. Use the console access to the existing and new switches to configure and verify correct device configuration.
Read more…
Question
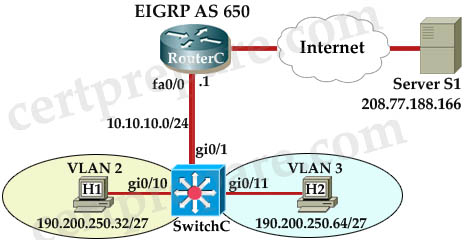
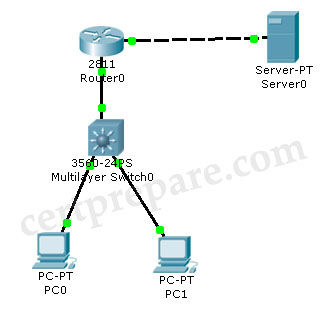
You have been tasked with configuring multilayer SwitchC, which has a partial configuration and has been attached to RouterC as shown in the topology diagram.
You need to configure SwitchC so that Hosts H1 and H2 can successful ping the server S1. Also SwitchC needs to be able to ping server S1. Due to administrative restrictions and requirements you should not add/delete VLANs, changes VLAN port assignments or create trunk links. Company policies forbid the use of static or default routing. All routes must be learned via EIGRP 650 routing protocol.
You do not have access to RouterC, RouterC is correctly configured. No trunking has been configured on RouterC.
Routed interfaces should use the lowest host on a subnet when possible. The following subnets are available to implement this solution:
– 10.10.10.0/24
– 190.200.250.32/27
– 190.200.250.64/27
Hosts H1 and H2 are configured with the correct IP address and default gateway.
SwitchC uses Cisco as the enable password.
Routing must only be enabled for the specific subnets shown in the diagram.
Answer and Explanation
Read more…
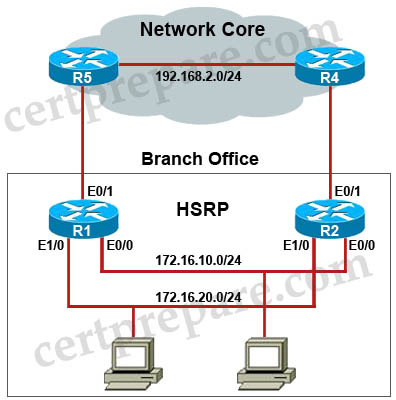
Refer to the topology below. R1 and R2 are configured to run HSRP. The network administrator wants to ask you about how HSRP operates in the vent of a device failure.
Read more…
Question:
The headquarter office for a cement manufacturer is installing a temporary Catalyst 3550 in an IDF to connect 24 additional users. To prevent network corruption, it is important to have the correct configuration prior to connecting to the production network. It will be necessary to ensure that the switch does not participate in VTP but forwards VTP advertisements that are received on trunk ports.
Because of errors that have been experienced on office computers, all nontrunking interfaces should transition immediately to the forwarding state of Spanning tree. Also, configure the user ports (all FastEthernet ports) so that the ports are permanently nontrunking.
Requirements:
You will configure FastEthernet ports 0/12 through 0/24 for users who belong to VLAN 20. Also, all VLAN and VTP configurations are to be completed in global configuration mode as VLAN database mode is being deprecated by Cisco. You are required to accomplish the following tasks:
1. Ensure the switch does not participate in VTP but forwards VTP advertisements received on trunk ports.
2. Ensure all non-trunking interfaces (Fa0/1 to Fa0/24) transition immediately to the forwarding state of Spanning-Tree.
3. Ensure all FastEthernet interfaces are in a permanent non-trunking mode.
4. Place FastEthernet interfaces 0/12 through 0/24 in VLAN 20.
Answer and Explanation:
Read more…
The title said it all. Below are the screenshots of the lab files
Files included:
+ MLS with EIGRP lab
+ LACP – STP Lab
Download these lab files from certprepare.com
Please say thanks to Jojo who created these lab-sims. Now you can practice with real SWITCH Lab questions.
Updated:
Ghost sent me a new version of these lab files (on Apr-30-2013) which include:
+ MLS with EIGRP lab
+ LACP – STP Lab
+ VTP Lab
+ VTP 2 lab
+ STP Lab
You can download it here and please say thanks to him:
Download new updated lab files from certprepare.com
Note: AAAdot1x sim is not supported in Packet Tracer so we can’t create one for you to practice.
Question:
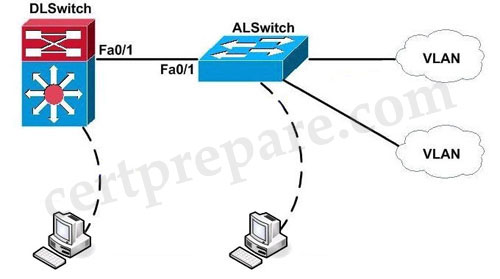
The headquarter offices for a book retailer are enhancing their wiring closets with Layer3 switches. The new distribution-layer switch has been installed and a new access-layer switch cabled to it. Your task is to configure VTP to share VLAN information from the distribution-layer switch to the access-layer devices. Then, it is necessary to configure interVLAN routing on the distribution layer switch to route traffic between the different VLANs that are configured on the access-layer switches; however, it is not necessary for you to make the specific VLAN port assignments on the access-layer switches. Also, because VLAN database mode is being deprecated by Cisco, all VLAN and VTP configurations are to be completed in the global configuration mode. Please reference the following table for the VTP and VLAN information to be configured:
Requirements:
| VTP Domain name |
cisco |
|
| VLAN Ids |
20 |
21 |
| IP Addresses |
172.16.71.1/24 |
172.16.132.1/24 |
These are your specific tasks:
1. Configure the VTP information with the distribution layer switch as the VTP server
2. Configure the VTP information with the access layer switch as a VTP client
3. Configure VLANs on the distribution layer switch
4. Configure inter-VLAN routing on the distribution layer switch
5. Specific VLAN port assignments will be made as users are added to the access layer switches in the future.
6. All VLANs and VTP configurations are to completed in the global configuration. To configure the switch click on the host icon that is connected to the switch be way of a serial console cable.
Answer and Explanation:
Read more…










