SD-WAN Architecture Questions
Question 1
Explanation
OMP advertises three types of routes:
+ OMP routes are prefixes that are learned from the local site, or service side, of a vEdge router. The prefixes are originated as static or connected routes, or from within the OSPF or BGP protocol, and redistributed into OMP so they can be carried across the overlay. OMP routes advertise attributes such as transport location (TLOC) information, which is similar to a BGP next-hop IP address for the route, and other attributes such as origin, originator, preference, site ID, tag, and VPN. An OMP route is only installed in the forwarding table if the TLOC to which it points is active.
+ TLOC routes are the logical tunnel termination points on the vEdge routers that connect into a transport network. A TLOC route is uniquely identified and represented by a three-tuple, consisting of system IP address, link color, and encapsulation (Generic Routing Encapsulation [GRE] or IPSec). In addition to system IP address, color, and encapsulation, TLOC routes also carry attributes such as TLOC private and public IP addresses, carrier, preference, site ID, tag, and weight. For a TLOC to be considered in an active state on a particular vEdge, an active BFD session must be associated with that vEdge TLOC.
+ Service routes represent services (firewall, IPS, application optimization, etc.) that are connected to the vEdge local-site network and are available for other sites for use with service insertion. In addition, these routes also include VPNs; the VPN labels are sent in this update type to tell the vSmart controllers what VPNs are serviced at a remote site.
Reference: https://explore.cisco.com/sd-wan-adopt/cvd-sd-wan-design-colors#page=7
Question 2
Explanation
The Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN image supports the following hardware platforms:
+ Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
+ Cisco 1000 Series ISRs
+ Cisco 4000 Series ISRs
+ Cisco 5400 ENCS
Question 3
Question 4
Explanation
For vEdge Cloud routers, vManage NMS can also sign certificates and generate bootstrap configurations, and it can decommission the devices.
Question 5
Explanation
By default, the control plane uses Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) as the protocol that provides privacy on all its tunnels. DTLS runs over UDP.
You can change the control plane security protocol to TLS, which runs over TCP. The primary reason to use TLS is that, if you consider the vSmart controller to be a server, firewalls protect TCP servers better than UDP servers.
Question 6
Explanation
Cisco vBond resides in the orchestration plane. The vBond controller is largely responsible for the Zero-Touch Provisioning process as well as first-line authentication, control/management information distribution, and facilitating Network Address Translation (NAT) traversal. When a router boots up for the first time in an unconfigured state, vBond is responsible for onboarding the device into the SD-WAN fabric. It is the job of vBond to understand how the network is constructed and then share that information amongst other components.
Question 7
Explanation
The vSmart controller is the brain of the overlay network, establishing, adjusting, and maintaining the connections that form the fabric of the overlay network. In these functions, it oversees the control plane of the Cisco SD-WAN overlay network. The vSmart controller participates only in the overlay network and has no direct peering relationships with any of the devices that an edge router is connected to on the host-facing side.
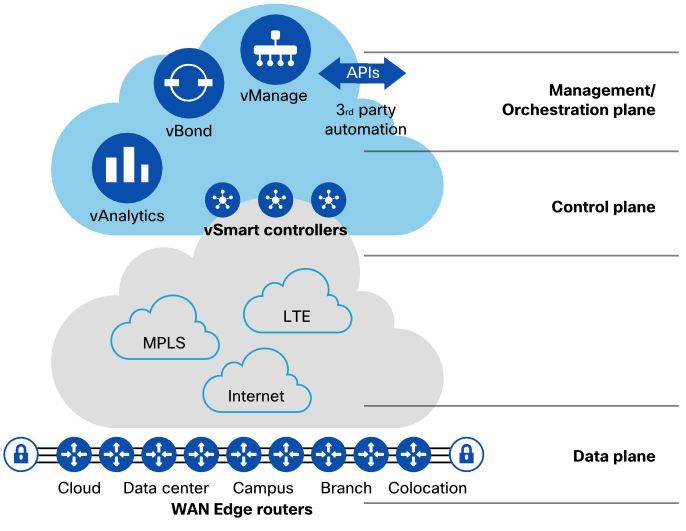
Question 8
Question 9
Question 10
Explanation
The data plane provides the infrastructure for sending data traffic among the vEdge routers in the Viptela overlay network. Data plane traffic travels within secure Internet Security (IPsec) connections. The Viptela data plane implements the key security components of authentication, encryption, and integrity in the following ways:
+ Authentication – As mentioned above, the Viptela control plane contributes the underlying infrastructure for data plane security. In addition, authentication is enforced by two other mechanisms:
++ RSA encryption with 2048-bit keys.
++ Two standard protocols from the IPsec security suite framework, Encapsulation Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH), are used to authenticate the origin of data traffic.



I can’t find the answers, please help me!
Wouldn’t questions 10 be C and D? I don’t understand how B (Transport Locations) is a valid choice.
Can please someone share the dumps. I have devnet dumps. Can exchange.
Question 10
Which two mechanisms are used to guarantee the integrity of data packets in the Cisco SD-WAN architecture data plane? (Choose two)
A. certificates
B. transport locations
C. authentication headers
D. encapsulation security payload
E. TPM chip
Answer: C , D
The data plane provides the infrastructure for sending data traffic among the vEdge routers in the Viptela overlay network. Data plane traffic travels within secure Internet Security (IPsec) connections. The Viptela data plane implements the key security components of authentication, encryption, and integrity in the following ways:
s00075.pngAuthentication—As mentioned above, the Viptela control plane contributes the underlying infrastructure for data plane security. In addition, authentication is enforced by two other mechanisms:
RSA encryption with 2048-bit keys.
Two standard protocols from the IPsec security suite framework, Encapsulation Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH), are used to authentication the origin of data traffic.
Encryption—The standard ESP protocol protects the data packet’s payload, and the standard AH protocol protects both the payload and the non-mutable header fields. Key exchange encryption is done using the AES-256 cipher.
Integrity—To guarantee that data traffic is transmitted across the network without being tampered with, the data plane implements several mechanisms from the IPsec security protocol suite:
The ESP protocol encapsulates the payload of data packets.
The HMAC-SHA1 algorithm, which is used by the IPsec AH protocol, combines a keyed-hash authentication code with SHA-1 cryptography to ensure data integrity. AH encapsulates the non-mutable fields in the outer IP header and the payload of data packets. You can configure the integrity methods supported on each vEdge router, and this information is exchanged in the router’s TLOC properties. If two vEdge peers advertise different authentication types, they negotiate the type to use, choosing the strongest method.
The anti-replay scheme protects against attacks in which an attacker duplicates encrypted packets.
rohl.. i can help u. i need devnet. i have sd-wan.
please reach out to me.
@jas how to contact you.. please email me on rbhagat009 g m a i llcom
@sam Cam you plz share the other questions?
Cleared exam. Simple questions. Someone with basic knowledge should be able to clear.
Q10:
As Sam mentioned, the correct answer seems C and D (authentication headers (AH) and encapsulation security payload (ESP)). The explanation from Cisco is as follows:
Data Plane Integrity
The following components contribute to the integrity of data packets in the Cisco SD-WAN data plane:
ESP, which is a standard IPsec encryption protocol, protects (via encryption and authentication) the inner header, data packet payload, and ESP trailer in all data packets. The modifications to ESP also protect the outer IP and UDP headers
Modifications to ESP, which protect (via authentication) the outer IP and UDP headers. This mimics the functionality of the AH protocol.
Anti-replay, which is also part of the standard IPsec software suite, provides a mechanism to number all data packets and to ensure that receiving routers accept only packets with unique numbers.
The first of these components, ESP, is the standard IPsec encryption protocol. ESP protects a data packet’s payload and its inner IP header fields both by encryption, which occurs automatically, and authentication. For authentication, ESP performs a checksum calculation on the data packet’s payload and inner header fields and places the resultant hash (also called a digest) into a 12-byte HMAC-SHA1 field at the end of the packet. (A hash is a one-way compression.) The receiving device performs the same checksum and compares its calculated hash with that in the packet. If the two checksums match, the packet is accepted. Otherwise, it is dropped. In the figure below, the left stack illustrates the ESP/UDP encapsulation. ESP encrypts and authenticates the inner headers, payload, MPLS label (if present), and ESP trailer fields, placing the HMAC-SHA1 hash in the ICV checksum field at the end of the packet. The outer header fields added by ESP/UDP are neither encrypted nor authenticated.
A second component that contributes to data packet integrity is the modifications to ESP to mimic AH. This modification performs a checksum that includes calculating the checksum over all the fields in the packet—the payload, the inner header, and also all the non-mutable fields in the outer IP header. AH places the resultant HMAC-SHA1 hash into the last field of the packet. The receiving device performs the same checksum, and accepts packets whose checksums match. In the figure below, the center stack illustrates the encapsulation performed by the modified version of ESP. ESP again encrypts the inner headers, payload, MPLS label (if present), and ESP trailer fields, and now mimics AH by authenticating the entire packet—the outer IP and UDP headers, the ESP header, the MPLS label (if present), the original packet, and the ESP trailer—and places its calculated HMAC-SHA1 hash into the ICV checksum field at the end of the packet.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/sdwan/configuration/security/vedge/security-book/security-overview.html#id_112388
@sam, @Anonymous: Thanks for your detection, we have just updated Q.10.
From where can I find the questions?
Questions are dated. Exam was updated late July.
Hi Has anyone passed this recently ???
Any one passed recently? The questions are updated?
Hi everyone. Does anyone have the up to date materials for 300-415?
@cwerprepare: Is there any new questions after September 10th, 2020 ?
All about Cisco SDWAN
https://www.thenetworkdna.com/search/label/Viptela%20SDWAN?&max-results=7
can’t see the questions , any advice
Just took the exam today and scored a 915. Thanks!!
Will you plz share the dumps.
Any one passed recently? The questions are updated?
Anyone took the exam recently? Certprepare updated questions. Any feedback ?
Are these questions still valid?
are they valid still the exam questions
Hello Guys where we can find the questions, above I am able to see answer only. can you please share the questions link.