Root Guard
Question 1
Explanation
Root guard does not allow the port to become a STP root port, so the port is always STP-designated. If a better BPDU arrives on this port, root guard does not take the BPDU into account and elect a new STP root. Instead, root guard puts the port into the root-inconsistent STP state which is equal to a listening state. No traffic is forwarded across this port.
Below is an example of where to configure Root Guard on the ports. Notice that Root Guard is always configure on designated ports.
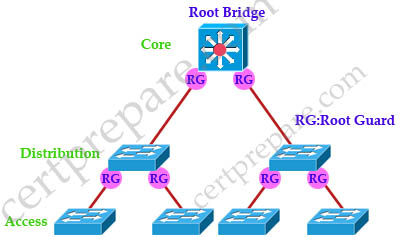
To configure Root Guard use this command:
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree guard root
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-protocol/10588-74.html
Question 2
Question 3
Question 4
Question 5
Question 6
Question 7
Question 8


