HSRP Questions 2
Here you will find answers to HSRP Questions – Part 2
Question 1
Three Cisco Catalyst switches have been configured with a first-hop redundancy protocol. While reviewing some show commands, debug output, and the syslog, you discover the following information:
| Jan 9 08:00:42.623: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Standby -> Active Jan 9 08:00:56.011: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Active -> Speak Jan 9 08:01:03.011: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Speak -> Standby Jan 9 08:01:29.427: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Standby -> Active Jan 9 08:01:36.808: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Active -> Speak Jan 9 08:01:43.808: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Speak -> Standby |
What conclusion can you infer from this information?
A. VRRP is initializing and operating correctly.
B. HSRP is initializing and operating correctly.
C. GLBP is initializing and operating correctly.
D. VRRP is not properly exchanging three hello messages.
E. HSRP is not properly exchanging three hello messages.
F. GLBP is not properly exchanging three hello messages.
Answer: E
Explanation
These error messages describe a situation in which a standby HSRP router did not receive three successive HSRP hello packets from its HSRP peer (by default, hello messages are sent every 3 seconds while the holdtime is 10 seconds). The output shows that the standby router moves from the standby state to the active state. Shortly thereafter, the router returns to the standby state. Unless this error message occurs during the initial installation, an HSRP issue probably does not cause the error message. The error messages signify the loss of HSRP hellos between the peers. When you troubleshoot this issue, you must verify the communication between the HSRP peers. A random, momentary loss of data communication between the peers is the most common problem that results in these messages. HSRP state changes are often due to High CPU Utilization. If the error message is due to high CPU utilization, put a sniffer on the network and the trace the system that causes the high CPU utilization.
(Reference and good resource: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk648/tk362/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094afd.shtml)
Question 2
You administer a network that uses two routers, R1 and R2, configured as an HSRP group to provide redundancy for the gateway. Router R1 is the active router and has been configured as follows:
| R1#configure terminal R1(config)#interface fa0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 10.10.0.5 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#standby 1 priority 150 R1(config-if)#standby preempt delay minimum 50 R1(config-if)#standby 1 track interface fa0/2 15 R1(config-if)#standby 1 ip 10.10.0.20 |
Which of the following describes the effect the “standby preempt delay minimum 50” command will have on router R1?
A. The HSRP priority for router R1 will increase to 200.
B. Router R1 will become the standby router if the priority drops below 50.
C. The HSRP priority for router R1 will decrease to 50 points when Fa0/2 goes down.
D. Router R1 will wait 50 seconds before attempting to preempt the active router.
Answer: D
Explanation
If R1, for some reason, loses its active state, the “standby preempt delay minimum 50” command will cause R1 to wait 50 seconds before it tries to get the active state again -> D is correct.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. HSRP has been configured and Link A is the primary route to router R4. When Link A fails, router R2 (Link B) becomes the active router. Which router will assume the active role when Link A becomes operational again?
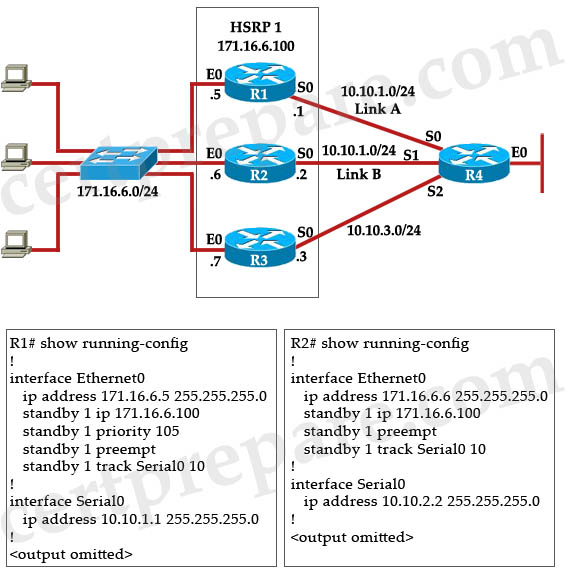
A. The primary router R1 will reassume the active role when it comes back online.
B. The standby router R2 will remain active and will forward the active role to router R1 only in the event of its own failure.
C. The standby router R2 will remain active and will forward the active role to router R1 only in the event of Link B failure.
D. The third member of the HSRP group, router R3, will take over the active role only in event of router R2 failure.
Answer: A
Explanation
When R1 fails, the “standby 1 preempt” command on R2 will cause R2 to take over the active state of R1. But when R1 comes up again, the “standby 1 preempt” command on R1 will help R1 take over the active state again. Without the “preempt” command configured on R2, R2 only takes over the active state only if it receives information indicating that there is no router currently in active state (by default it does not receive 3 hello messages from the active router). Without the “preempt” command on R2, it will not become active router even if its priority is higher than all other routers.
Question 4
Which first-hop redundancy solution listed would supply clients with MAC address 0000.0C07.AC0A for group 10 in response to an ARP request for a default gateway?
A. IRDP
B. Proxy ARP
C. GLBP
D. HSRP
E. VRRP
F. IP Redirects
Answer: D
Explanation
The last two-digit hex value in the MAC address presents the HSRP group number. In this case 0A in hexa equals 10 in decimal so this router belongs to group 10 and it is running HSRP.
Question 5
What three tasks will a network administrator perform to successfully configure Hot Standby Routing Protocol? (Choose three)
A. Define the encapsulation type
B. Define the standby router
C. Define the IP address
D. Enable the standby mode
E. Enable HSRP
Answer: B C E
Question 6
You want to allow Router R1 to immediately become the active router if its priority is highest than the active router fails. What command would you use if you wanted to configure this?
A. en standby 1 preempt
B. standby 1 preempt enable
C. standby 1 preempt
D. hot standby 1 preempt
Answer: C
Question 7
Routers R1 and R2 are configured for HSRP as shown below:
Router R1:
| interface ethernet 0 ip address 20.6.2.1 255.255.255.0 standby 35 ip 20.6.2.21 standby 35 priority 100 ! interface ethernet 1 ip address 20.6.1.1 255.255.255.0 standby 34 ip 20.6.1.21 |
Router R2:
| interface ethernet 0 ip address 20.6.2.2 255.255.255.0 standby 35 ip 20.6.2.21 ! interface ethernet 1 ip address 20.6.1.2 255.255.255.0 standby 34 ip 20.6.1.21 standby 34 priority 100 |
You have configured the routers R1 & R2 with HSRP. While debugging router R2 you notice very frequent HSRP group state transitions. What is the most likely cause of this?
A. physical layer issues
B. no spanning tree loops
C. use of non-default HSRP timers
D. failure to set the command standby 35 preempt
Answer: A
Explanation
The configuration on both R1 and R2 are correct. But both routers are not configured with the “preempt” command so by default they only take over the active state when they believe there is no active router (by default they don’t hear 3 successive hello messages from the active router). Therefore the most likely cause of this problem is a link failure between them (physical layer issue) -> A is correct.
Question 8
In which three HSRP states do routers send hello messages? (Choose three)
A. Learn
B. Speak
C. Standby
D. Listen
E. Active
F. Remove
Answer: B C E
Explanation
Speak state: sends hello messages to compete for the standby or active role.
Standby state: send hello messages to inform it is the standby router so that other routers (which are not active or standby router, in listen state) know the standby router is still there.
Active state: sends hello messages to indicate it is still up
Question 9
In the hardware address 0000.0c07.ac0a, what does 07.ac represent?
A. HSRP well-known physical MAC address
B. Vendor code
C. HSRP router number
D. HSRP group number
E. HSRP well-known virtual MAC address
Answer: E
Explanation
The HSRP standby IP address is a virtual MAC address which is composed of 0000.0c07.ac**. In which “**” is the HSRP group number in hexadecimal.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. Which two problems are the most likely cause of the exhibited output? (Choose two)
| Vlan8 – Group 8 Local state is Active, priority 110, may preempt Hellotime 3 holdtime 10 Next hello sent in 00:00:01.168 Hot standby IP address is 10.1.2.2 configured Active router is local Standby router is unknown expired Standby virtual mac address is 0000.0c07.ac08 5 state changes, last state change 00:05:03 |
A. Transport layer issues
B. VRRP misconfiguration
C. HSRP misconfiguration
D. Physical layer issues
E. Spanning tree issues
Answer: C D
Explanation
When you see this error, it means the local router fails to receive HSRP hellos from neighbor router. Two things you should check first are the physical layer connectivity and verify the HSRP configuration. An example of HSRP misconfiguration is the mismatched of HSRP standby group and standby IP address.
Another thing you should check is the mismatched VTP modes.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk648/tk362/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094afd.shtml)


