Security Questions
Here you will find answers to Security Questions
Question 1
Which two components should be part of a security implementation plan? (Choose two)
A. detailed list of personnel assigned to each task within the plan
B. a Layer 2 spanning-tree design topology
C. rollback guidelines
D. placing all unused access ports in VLAN 1 to proactively manage port security
E. enabling SNMP access to Cisco Discovery Protocol data for logging and forensic analysis
Answer: B C
Explanation
Implementing a security plan includes:
+ STP design topology
+ Rollback guidelines
+ Summary and detailed implementation steps
+ Incident response plan
+ Security policy
Question 2
Which description correctly describes a MAC address flooding attack?
A. The attacking device crafts ARP replies intended for valid hosts. The MAC address of the attacking device then becomes the destination address found in the Layer 2 frames sent by the valid network device.
B. The attacking device crafts ARP replies intended for valid hosts. The MAC address of the attacking device then becomes the source address found in the Layer 2 frames sent by the valid network device.
C. The attacking device spoofs a destination MAC address of a valid host currently in the CAM table. The switch then forwards frames destined for the valid host to the attacking device.
D. The attacking device spoofs a source MAC address of a valid host currently in the CAM table. The switch then forwards frames destined for the valid host to the attacking device.
E. Frames with unique, invalid destination MAC addresses flood the switch and exhaust CAM table space. The result is that new entries cannot be inserted because of the exhausted CAM table space, and traffic is subsequently flooded out all ports.
F. Frames with unique, invalid source MAC addresses flood the switch and exhaust CAM table space. The result is that new entries cannot be inserted because of the exhausted CAM table space, and traffic is subsequently flooded out all ports.
Answer: F
Explanation
MAC flooding attack is a technique in which the attacker floods the switch with packets, each containing different source MAC address. This makes the switch learn the MAC addresses until its memory is used up. Now the switch acts like a hub, in which all incoming packets are broadcast out on all ports instead of just to the correct destination port as normal operation. The attacker can listen to these broadcast packets and capture sensitive data.
Question 3
By itself, what does the command “aaa new-model” enable?
A. It globally enables AAA on the switch, with default lists applied to the VTYs.
B. Nothing; you must also specify which protocol (RADIUS or TACACS) will be used for AAA.
C. It enables AAA on all dot1x ports.
D. Nothing; you must also specify where (console, TTY, VTY, dot1x) AAA is being applied.
Answer: A
Explanation
Before you can use any of the services Authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) network security services provide, you must enable AAA. Enable AAA by using the aaa new-model global configuration command.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.
| Switch# configure terminal Switch(config)# interface gigabitethemet0/1 Switch(config-if)# ip verify source port-security Switch(config-if)# exit Switch(config)# ip source binding 0100.0022.0010 vlan 10 10.0.0.2 interface gigabitethernet0/1 Switch(config)# ip source binding 0100.0230.0002 vlan 11 10.0.0.4 interface gigabitethernet0/1 Switch(config)# end |
Which two statements about this Layer 3 security configuration example are true? (Choose two)
A. Static IP source binding can be configured only on a routed port.
B. Source IP and MAC filtering on VLANs 10 and 11 will occur.
C. DHCP snooping will be enabled automatically on the access VLANs.
D. IP Source Guard is enabled.
E. The switch will drop the configured MAC and IP address source bindings and forward all other traffic.
Answer: B D
Explanation
The command “ip verify source port-security” enables IP source guard (on Gi0/1) -> D is correct. Notice that without the keyword “port-security”, the switch only inspects source IP address. With the keyword “port-security”, the source MAC address is also inspected -> B is correct.
Question 5
Which statement is true about Layer 2 security threats?
A. MAC spoofing, in conjunction with ARP snooping, is the most effective counter-measure against reconnaissance attacks that use Dynamic ARP Inspection to determine vulnerable attack points.
B. DHCP snooping sends unauthorized replies to DHCP queries.
C. ARP spoofing can be used to redirect traffic to counter Dynamic ARP Inspection.
D. Dynamic ARP Inspection in conjunction with ARP spoofing can be used to counter DHCP snooping attacks.
E. MAC spoofing attacks allow an attacking device to receive frames intended for a different network host.
F. Port scanners are the most effective defense against Dynamic ARP Inspection.
Answer: E
Explanation
Attacking device spoofs the MAC address of a valid host currently in the CAM table. The switch then forwards frames destined for the valid host to the attacking device -> E is correct.
Question 6
A network is deployed using recommended practices of the enterprise campus network model, including users with desktop computers connected via IP phones. Given that all components are QoS-capable, where are the two optimal locations for trust boundaries to be configured by the network administrator? (Choose two)
A. host
B. IP phone
C. access layer switch
D. distribution layer switch
E. core layer switch
Answer: B C
Explanation
The perimeter formed by switches that do not trust incoming QoS is called the trust boundary (or in other words, trust boundary is the interface where the marking on a packet is trusted). Trust boundary should be as close to the edge as possible. In a large network, the distribution layer switches are often heavily loaded so it is better to apply QoS to IP Phone or access layer switch (which are responsible for lesser traffic).
If we trust from the IP Phone, when data from hosts reach the IP Phone, the switch will ignore the CoS/ToS markings and consider all data packets to have a value of 0.
Answer A is not correct because a trust boundary at the host is not trustworthy.
Note:
To understand the concept of a trust boundary, you must first have a basic understanding of QoS markings. As a device sends traffic, that
traffic may or may not have QoS markings attached to it. These markings may or may not be trustworthy. For example, a Cisco IP phone marks all of its traffic with an extremely high priority. In this case, the markings are trustworthy because the audio traffic from the phone does indeed need high-priority service. However, a technology-savvy user might configure a computer to mark traffic from it with the same high-priority marking as the voice traffic. In this case, the marking is not trustworthy.
Now we can jump back to the concept of a trust boundary. The trust boundary is the point of the network where you begin trusting that the network traffic is accurately identified with the correct QoS marking. Depending on the capabilities of the devices on your network, you can you can begin applying QoS markings close to the user devices, as shown in the picture below.
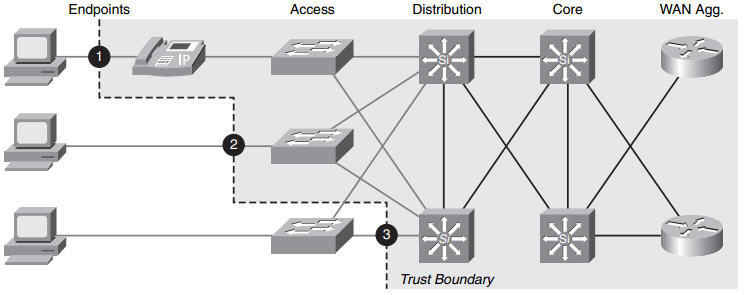
Cisco IP phones have the ability to mark their own traffic as high priority and strip any high-priority markings from traffic sent by the attached PC. If you are using the Cisco IP phone to mark traffic, you have extended the trust boundary to point 1 shown in the picture above. This is the ideal trust point because it distributes the QoS marking process to many Cisco IP phones rather than forcing the switches to apply QoS markings to a higher volume of traffic. If you have PCs attached to the network and you have access layer switches with QoS capabilities, you can begin marking at these devices (this is point 2 in the figure above). If your access layer switches do not have QoS capabilities, then the first possible place you can apply QoS markings is at the distribution layer switches (shown as point 3 in the picture above). This will work just fine; however, it adds an extra load to the distribution layer switches. Likewise, you will have network traffic passing through access layer switches without any QoS treatment. Although this is usually a safe bet – because access layer switches typically have higher-speed connections, on which congestion is rare – it is always best to apply QoS in as many places as possible where there is a potential bottle-neck.
(Reference: CCNA Voice Official Exam Certification Guide)
Question 7
Which optional feature of an Ethernet switch disables a port on a point-to-point link if the port does not receive traffic while Layer 1 status is up?
A BackboneFast
B. UplinkFast
C. Loop Guard
D. UDLD aggressive mode
E. Fast Link Pulse bursts
F. Link Control Word
Answer: D
Explanation
UDLD is a Layer 2 protocol that enables devices to monitor the physical configuration of the cables and detect when a unidirectional link exists. UDLD detects a unidirectional link by sending periodic hellos out to the interface. UDLD supports two modes of operation: normal (the default) and aggressive.
In normal mode, if the interfaces are connected correctly but the traffic is one way, UDLD does not detect the unidirectional link because the Layer 1 mechanism, which is supposed to detect this condition, does not do so. In case, the logical link is considered undetermined, and UDLD does not disable the interface.
In aggressive mode, UDLD detects a unidirectional link by using the previous detection methods. UDLD in aggressive mode can also detect a unidirectional link on a point-to-point link on which no failure between the two devices is allowed. In these cases, UDLD shuts down the affected interface.
Note: Aggressive mode is the recommended mode when configuring UDLD.
Question 8
Which statement about 802.1x port-based authentication is true?
A. Hosts are required to have an 802.1x authentication client or utilize PPPoE.
B. Before transmitting data, an 802.1x host must determine the authorization state of the switch.
C. RADIUS is the only supported authentication server type.
D. If a host initiates the authentication process and does not receive a response, it assumes it is not authorized.
Answer: C
Explanation
For 802.1x port-based authentication, the Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) security system with Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) extensions is the only supported authentication server; it is available in Cisco Secure Access Control Server version 3.0. RADIUS operates in a client/server model in which secure authentication information is exchanged between the RADIUS server and one or more RADIUS clients.
Question 9
What is needed to verify that a newly implemented security solution is performing as expected?
A. a detailed physical and logical topology
B. a cost analysis of the implemented solution
C. detailed logs from the AAA and SNMP servers
D. results from audit testing of the implemented solution
Answer: D
Explanation
Verifying a security solution includes two points:
+ Verification of an implemented security solution requires results from audit testing of the implemented solution
+ Verifying a documentation for rollback plan
Question 10
Which Cisco IOS command globally enables port-based authentication on a switch?
A. aaa port-auth enable
B. radius port-control enable
C. dot1x system-auth-control
D. switchport aaa-control enable
Answer: C
Explanation
We must enable 802.1X authentication for the entire system before configuring it for individual ports. After you globally enable 802.1X authentication, you can configure individual ports for 802.1X authentication if they meet the specific requirements that are required by 802.1X.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst4000/8.3and8.4glx/configuration/guide/8021x.html)


